The Rise of Connected Data and the Connected Enterprise
What's covered in this article?
Cluedin articles


Augmented Data Quality (ADQ) leverages advanced technologies such as AI and ML to enhance traditional data management practices. It automates the detection and correction of data issues, enabling data leaders, data stewards, and domain experts to ensure higher data accuracy, consistency, and reliability. This approach is vital in today's fast-paced data environments, where manual oversight is impractical due to the sheer volume and complexity of data. ADQ represents a shift towards more dynamic, responsive data governance models, aligning closely with strategic business objectives by providing a cleaner, more trustworthy data foundation.
ADQ becomes crucial in various scenarios, such as when organizations face rapid data growth, deal with data from multiple, disparate sources, or require real-time data analysis for decision-making. It's also essential when businesses undertake digital transformation projects that necessitate clean, reliable data for new applications. In addition, industries regulated by strict data compliance standards need augmented solutions to ensure accuracy and adherence to regulations. Essentially, any situation where the volume, velocity, or variety of data overwhelms traditional management approaches calls for augmented data quality solutions.

Enterprises constantly seek solutions that not only streamline their data processes but also align seamlessly with their existing technology stack. For businesses that have committed to the Microsoft Azure ecosystem, CluedIn is the go-to Master Data Management (MDM) solution. Here we explore five fundamental reasons why CluedIn stands as the most natural choice for Master Data Management on Microsoft Azure.
New CluedIn AI Assistant helps organizations to integrate data 60% faster, validate and deduplicate data 50% quicker, and improve overall data quality by 30%
CluedIn today announced that its new release is now available in private preview with an anticipated GA date of early 2024. The latest version represents another significant leap forward in reinforcing CluedIn’s position as the most advanced MDM system available, in terms of both enabling domain experts and accelerating the process of extracting value from enterprise data.
Your personal MDM assistant
In an industry first, CluedIn now includes an AI Assistant feature to support data stewards, engineers, and domain experts with the day-to-day management and operationalization of data. The CluedIn AI Assistant will help with the generation of rules, mapping, and providing additional context to specific pieces of data. CluedIn customers can also expect AI-aided generation of deduplication rules and project recommendations in the near future. Learn more about how the CluedIn AI Assistant could help you save days of manual effort and aid in bridging the data literacy gap here.
The new release builds on CluedIn’s commitment to pioneering the use of Generative AI in MDM, as demonstrated by the announcement that CluedIn was the first MDM vendor to integrate with Azure OpenAI in April 2023.
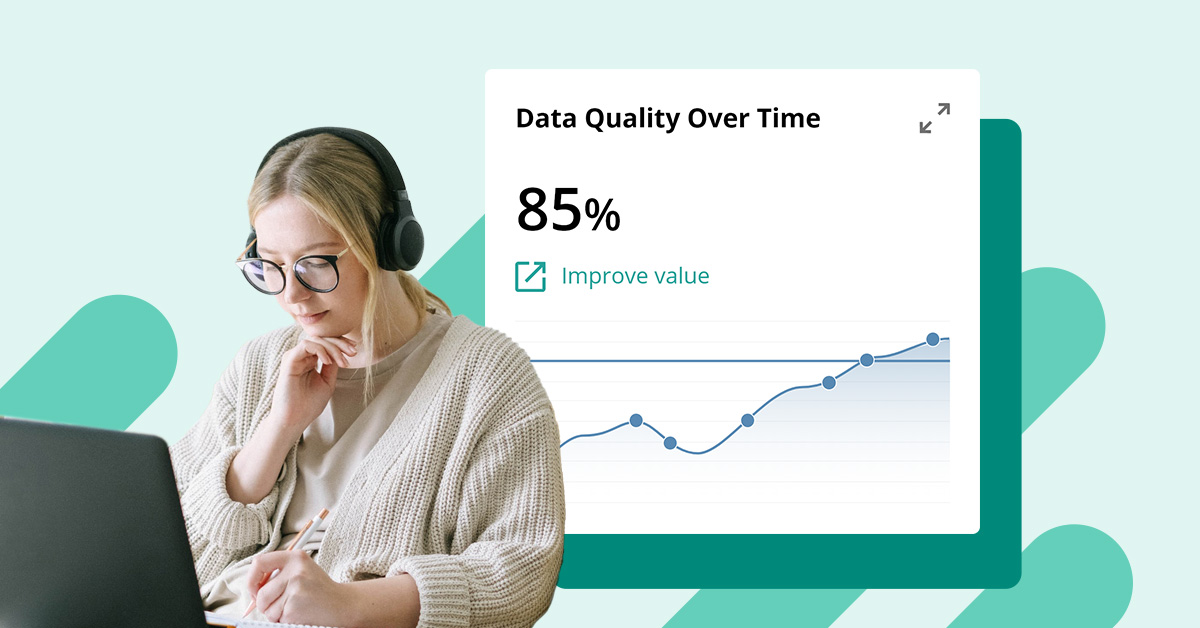
The quality of your data can make or break your business. While Master Data Management (MDM) solutions are often touted as the go-to for ensuring high-quality data, it is possible to make improvements without them.
Here are six ways to increase the quality of your data without using an MDM solution:

Tradition dictates that there certain types of data that should be handled by a Master Data Management (MDM) platform, and others that shouldn’t. However, the sheer diversity and complexity of data mean that these notions are being challenged, as organizations realize that in order to achieve a comprehensive and actionable view of any domain, they need the bigger picture.
Before we examine the types of data that an MDM solution is suitable for, we should first define the different data types:
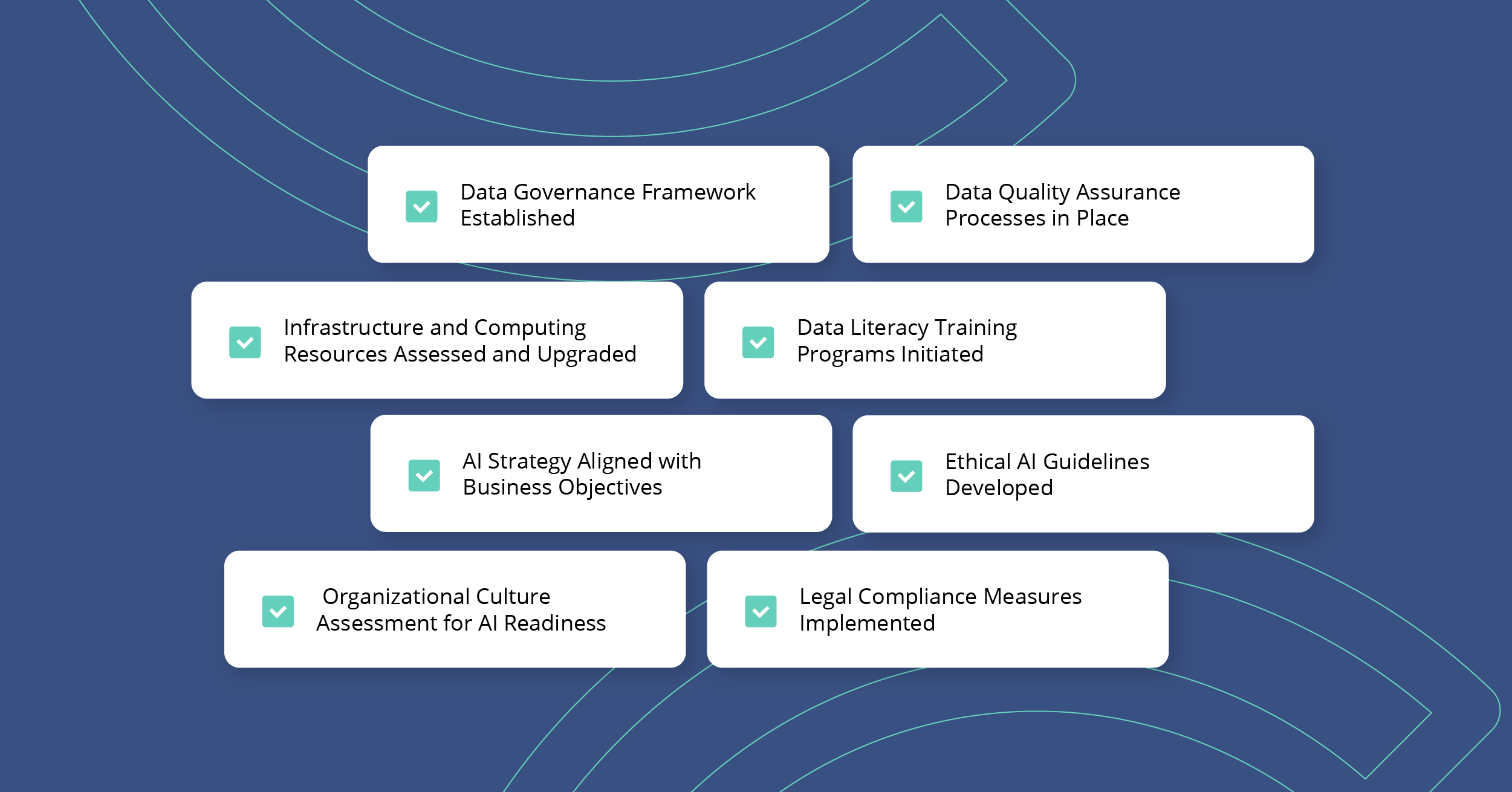
The advent of Artificial Intelligence (AI) has ushered in a new era of technological innovation, offering unprecedented opportunities for businesses to enhance efficiency, innovation, and competitiveness. However, the journey to becoming AI-ready involves navigating a complex landscape of technical, organizational, and cultural challenges. The guide below and the subsequent checklist provide actionable advice for data leaders and practitioners on preparing their organizations to incorporate AI.
Enhance Data Accessibility and Quality
Upgrade Infrastructure and Computing Resources:
Boost Data Literacy Across the Organization
Cultivate an AI-Ready Culture
Address Ethical and Legal Concerns
Strategic AI Implementation Planning
Overcome Resistance to Change
Foster a Collaborative Environment

This week, the annual Microsoft Ignite conference is taking place in Seattle. One of the main announcements to come out of the show is the General Availability of Microsoft Fabric, and an expansion of its governance and security capabilities through a tighter integration with Microsoft Purview.
As the preferred Master Data Management partner for Microsoft Azure customers, CluedIn is already fully integrated with both Microsoft Fabric and Purview. In combination with Microsoft Purview, we offer a unified, scalable, and transparent way to manage and drive insights from data. For Microsoft Fabric customers, we take raw data and make it ready for analysis by any tool in the Fabric suite. We also do this 80% faster than any other Master Data Management Platform on the market.
Bringing Microsoft Fabric and Purview together is the next natural step in helping businesses manage their end-to-end data estate with ultimate security, assurance, and accessibility. Microsoft Fabric is redefining how teams work with data by bringing everyone together on a single, AI-powered platform built for the era of AI. With Purview and CluedIn providing the pipeline of high-quality, trusted data needed to fuel Fabric, a new data and analytics powerhouse has emerged.
The value that engineers bring to the data stack is undeniable. They play a crucial role in ensuring data is primed for insights. However, the immense value and necessity of involving Domain Experts in the data supply chain, not merely as consumers but as contributors, cannot be overstated.
IT and Engineering have distinct focuses within the data supply chain. Their work aligns with the overarching goal of preparing data for insights. Yet, there's a specific persona that is interested in enhancing the intrinsic value of the data itself. Consider the analogy of a Netflix movie director. While Netflix's ability to deliver content globally, start streaming in seconds, and function across devices is impressive, the content—the movie—remains the star. It requires directors, writers, and editors to refine the content to the point where it captivates the audience. Similarly, one might ask, who is the "director" for your customer data?
During its 30-year history, many myths have arisen around Master Data Management (MDM), some of which may have been valid in the early days but are no longer true today. MDM has come a long way, and is experiencing something of a renaissance as progressive platforms take advantage of technical innovations like Graph databases and Generative AI, and offer increased commercial flexibility via the major CSPs.
Join us as we expose the eight most common MDM myths below, and discover how MDM has developed to become more accessible, manageable, and impactful.